FUNCTIONAL TESTING OF DIODES
The test just mentioned tests the diode for forward bias operation. No diode test would be complete without a reverse bias test as well.
Diodes can be tested with a Digital Multimeter (DMM) to determine either:
if they are working correctly, or
whether they are germanium or silicon.
Most modern DMMs have a setting specifically for testing diodes.
This setting is identified on the DMM's dial by the diode symbol.
When they DMM's positive red lead is connected to the diode's anode and the DMM's blue (or black) negative lead is connected to the diode's cathode, a reading of approximately 0.3 V indicates the diode is germanium, a reading of approximately 0.7 V indicates the diode is silicon and a reading significantly different from either of these would indicate the diode is defective.
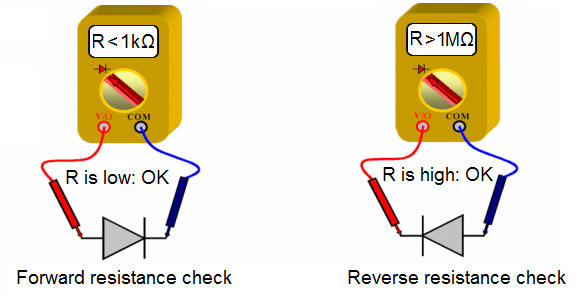
In ohmmeter position, DMM indicates a low resistance.
Simply reverse the diode so the positive red lead connects to the cathode of the diode and the blue (or black) negative Tip lead connects to the anode of the diode. When reverse biased, the ohmmeter should indicate that no current is flowing through the diode.
If current does flow through the diode when it is reversed biased, the diode is defective.
In ohmmeter position, DMM indicates a high resistance.
Forward biased diodes will have very little resistance; reverse biased diode will have significant resistance.
If either of two readings are not as specified diode is faulty. Replace.