DETAILED OPERATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SCHOTTKY DIODES
The Schottky diode or Schottky Barrier diode is an electronics component that is widely used for radio frequency (RF) applications as a mixer or detector diode.
The Schottky diode is also used in power applications as a rectifier, again because of its low forward voltage drop leading to lower levels of power loss compared to ordinary PN junction diodes.
Although normally called the Schottky diode these days, named after Schottky, it is also sometimes referred to as the surface barrier diode, hot carrier diode or even hot electron diode.
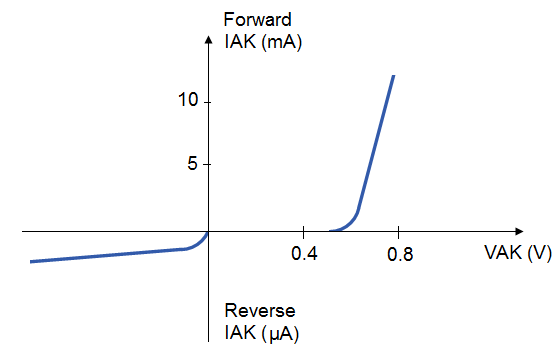
3.1. Symbol and characteristics:
The schematic symbol for a Schottky diode is shown in figure below.

Forward voltage drop and junction capacitance (CJ) of Schottky diodes are closer to ideal than the average “rectifying” diode. This makes them well suited for high-frequency applications. Unfortunately, Schottky diodes typically have lower forward current (IF) and reverse voltage ratings than rectifying diodes and are thus unsuitable for applications involving substantial amounts of power. Though they are used in low voltage switching regulator power supplies.
Schottky diode technology finds broad application in high-speed computer circuits, where the fast switching time equates to high speed capability, and the low forward voltage drop equates to less power dissipation when conducting.
Commonly encountered Schottky diodes include the 1N5817 series 1 A rectifiers. Schottky metal-semiconductor junctions are featured in the successors to the 7400 TTL family of logic devices, the 74S, 74LS and 74ALS series, where they are employed as clamps in parallel with the collector-base junctions of the bipolar transistors to prevent their saturation, thereby greatly reducing their turn-off delays.
3.2. Applications:
The Schottky barrier diodes are widely used in the electronics industry finding many uses as diode rectifier. Its unique properties enable it to be used in a number of applications where other diodes would not be able to provide the same level of performance. In particular it is used in areas including:
RF mixer and detector diode: The Schottky diode has come into its own for radio frequency applications because of its high switching speed and high frequency capability. In view of this Schottky barrier diodes are used in many high performance diode ring mixers. In addition to this their low turns on voltage and high frequency capability and low capacitance make them ideal as RF detectors.
Power rectifier: Schottky barrier diodes are also used in high power applications, as rectifiers. Their high current density and low forward voltage drop mean that less power is wasted than if ordinary PN junction diodes were used. This increase in efficiency means that less heat has to be dissipated, and smaller heat sinks may be able to be incorporated in the design.
Power OR circuits: Schottky diodes can be used in applications where a load is driven by two separate power supplies. One example may be a mains power supply and a battery supply. In these instances it is necessary that the power from one supply does not enter the other.
This can be achieved using diodes. However it is important that any voltage drop across the diodes is minimised to ensure maximum efficiency. As in many other applications, the Schottky diode is ideal for this in view of its low forward voltage drop.
Schottky diodes tend to have a high reverse leakage current. This can lead to problems with any sensing circuits that may be in use. Leakage paths into high impedance circuits can give rise to false readings. This must therefore be accommodated in the circuit design.
Solar cell applications: Solar cells are typically connected to rechargeable batteries, often lead acid batteries because power may be required 24 hours a day and the Sun is not always available. Solar cells do not like the reverse charge applied and therefore a diode is required in series with the solar cells.
Any voltage drop will result in a reduction in efficiency and therefore a low voltage drop diode is needed. As in other applications, the low voltage drop of the Schottky diode is particularly useful, and as a result Schottky diodes are normally used in this application.
Clamp diode - especially with its use in LS TTL: Schottky barrier diodes may also be used as a clamp diode in a transistor circuit to speed the operation when used as a switch. They were used in this role in the 74LS (low power Schottky) and 74S (Schottky) families of logic circuits. Schottky barrier diodes are inserted between the collector and base of the driver transistor to act as a clamp. To produce a low or logic "0" output the transistor is driven hard on, and in this situation the base collector junction in the diode is forward biased.
When the Schottky diode is present this takes most of the current and allows the turn off time of the transistor to be greatly reduced, thereby improving the speed of the circuit.