DETAILED OPERATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF RECTIFIER DIODES
Rectifier diodes are used in power supplies to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), a process called rectification. They are also used elsewhere in circuits where a large current must pass through the diode.
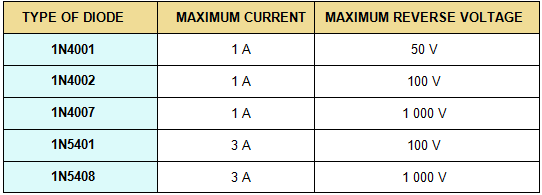
All rectifier diodes are made from silicon and therefore have a forward voltage drop of 0.7 V. The table shows maximum current and maximum reverse voltage for some popular rectifier diodes. The 1N4001 is suitable for most low voltage circuits with a current of less than 1 A.
Performance specifications for rectifier diodes include average rectified current, reverse current, forward voltage, peak forward surge current, reverse recovery time, and junction operating temperature.
Average rectified current (Io) is the maximum allowable continuous average current in the forward direction under specified conditions.
Reverse current or leakage current (IR), the current at which the specified reverse voltage is applied, measures the current that flows when reverse bias is applied to a semiconductor junction.
Forward voltage (VF) is the voltage across the diode terminals resulting from the flow of current in the forward direction.
Peak forward surge current (PFSM) is the maximum allowable surge value of forward current without repetition.
Reverse recovery time (RRT) is the time taken for the reverse current (IR) to reach a specified level when the reverse voltage is applied while the device is conducting in the forward direction. Junction operating temperature (Tj) is the range of temperatures at which diode are designed to operate.